Most aromatic amino
acids in plants are formed by three main types of aromatic acids;
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
These three important
aromatic amino acids are exclusively synthesized by Shikimic acid pathway that
is unique to plants and microbes. This pathway got its name by an important
intermediate forms,called Shikimic acid.
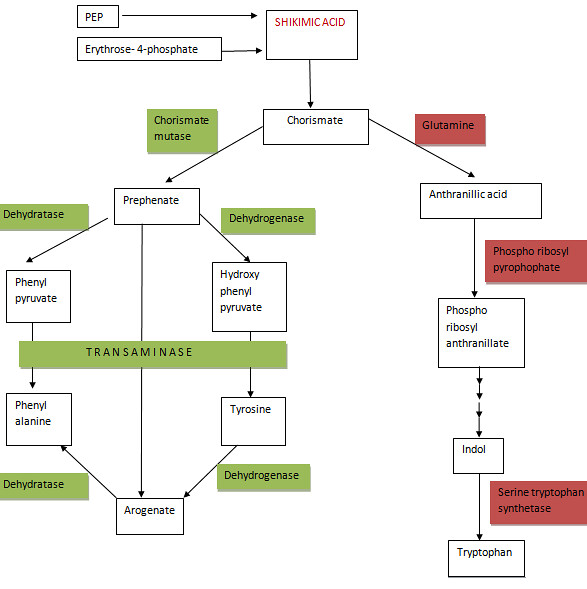
Shikimic acid pathway
starts from the condensation of Erythrose-4-phosphate with Phosphoenolpyruvate
(PEP). PEP is provided by the glycolysis while Erythrose-4-P comes from either oxidative
pentose phosphate pathway or Calvin cycle. Therefore Shikimic acid pathway is combined
with other important metabolic pathways of the cell.
The condensation produces
3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonic acid-7-phosphate (DAHP). DAHP undergoes another
series of reactions including condensation with another molecule of PEP to give
out Chorismic acid. Shikimic acid forms as an intermediate in this reaction and
regarded as the key intermediate.
Chorismate is a
central intermediate giving rise to two products; Prephenate and Anthranillic
acid. Shikimic acid pathway is shown simply as below.
The synthesis of aromatic amino acids is important as these amino acids are the precursors for the synthesis of defense and repair compounds.
Phenylalanine
·
Flavonoids:
in plant pigments (eg: Anthocyanine), act against pathogens. Antioxidants.
·
Coumarins:
Has appetite-suppressing properties.
·
Liginin:
In lignicolous fungi
Tyrosine
·
Tocopherol:
Antioxidant in cornifers.
·
Plastoquinone:
Important in photosynthesis.
·
Cyanogenic
glucosides: Phytoanticipants. Important in plant defense against herbivores due
to bitter taste and release of toxic hydrogen cyanide upon tissue disruption.
Tryptophan
·
Alkaloides:
provides protection as it prevents insects and herbivores eating the plant.
·
Plant
growth regulators
Hello, the whole thing is going perfectly here, that’s truly good, keep up writing.
ReplyDelete